RESTORATIVE
JUSTICE IN
ABBOTSFORD
BEGAN
IN 2001

Restorative Justice
What It Is
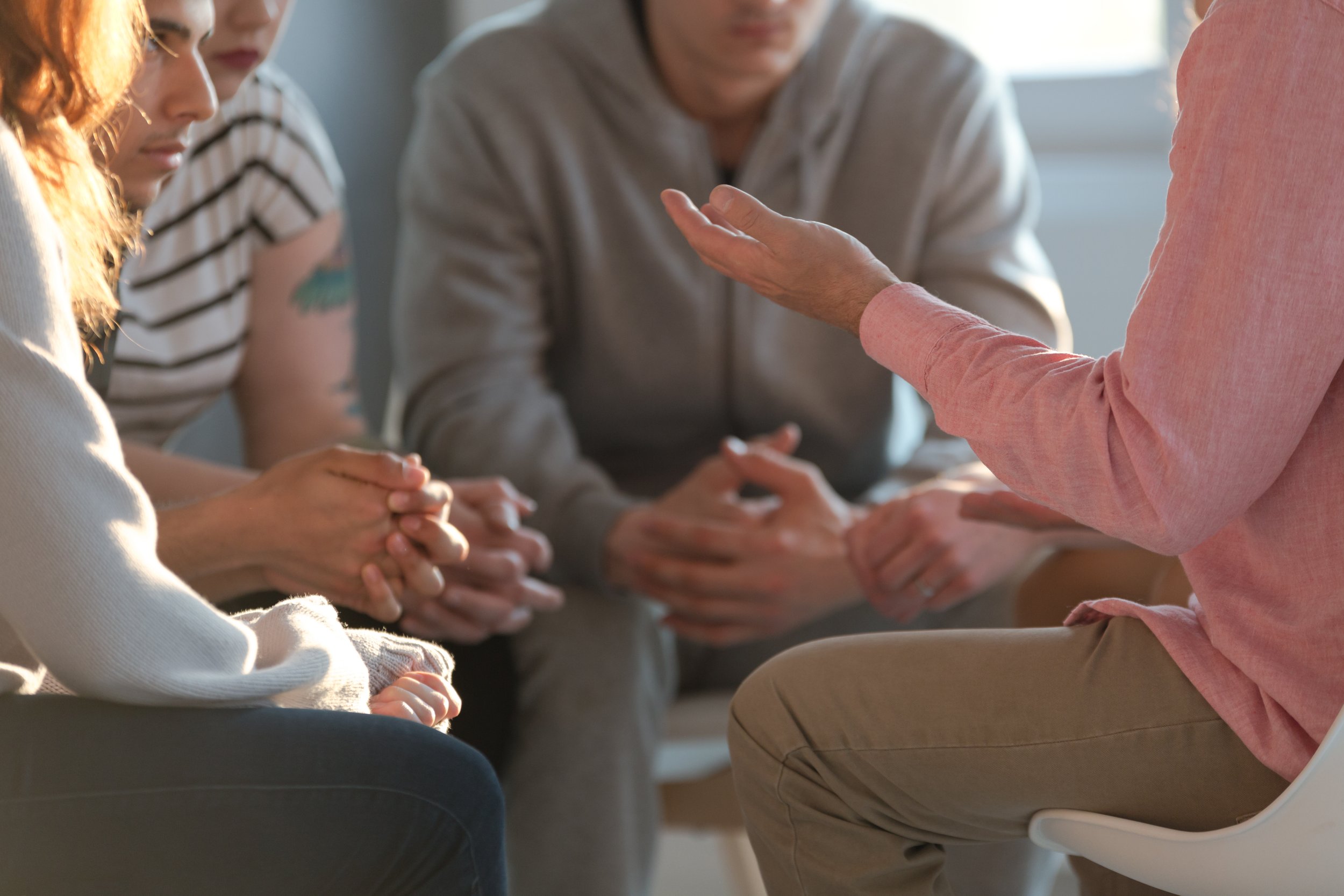
The practice of Restorative Justice (RJ) views crime as harm done to people and relationships, rather than simply the breaking of laws. Recognizing that a criminal or harmful act creates an obligation to make things right, a restorative justice process seeks both to give those harmed a meaningful voice in the reparative process and to provide those responsible for harm with an opportunity to make amends.
Restorative Justice understands that individuals most directly impacted by crime often have a need for answers, a desire to understand what happened and why, and an opportunity to express the effects and impacts of the harm. They may also seek healing, closure, and a sense of resolution. Where the traditional court process often falls short in meeting these needs, restorative justice offers a safely guided process in which those harmed can have influence and input into how the harm will be addressed.
Engaging in a restorative justice process also means meeting the needs of the responsible party. “High accountability and high support” are two hallmarks of a healthy process—one that holds individuals accountable for their behaviour while also providing the support necessary to face those they have harmed and to make meaningful amends. This support includes helping responsible parties reconnect with their community in a way that is reintegrative rather than shaming or isolating.
Facing those harmed and answering for one’s actions can be an extremely difficult and emotional experience. Yet it is within this powerful encounter that empathy and understanding can begin to grow. Seeing one another beyond judgments, assumptions, and labels creates the possibility of connection, and it is in this light that reconciliation and resolution can take place.
Ultimately, restorative justice responds to harm with the overarching goal of promoting equitable, healthy relationships among individuals and within communities.
The Restorative Justice process focusses on what needs to be done to address the way people in the community have been harmed and impacted by an offence. It provides a safe and respectful opportunity for affected parties to have a voice in the justice process and to dialogue with those responsible, leading to greater levels of accountability, as well as, transformation and learning. Underlying issues and causes that contributed to the offence are also considered. The goal is an agreement that repairs the harm done to those impacted, supports rebuilding of relationships, restoring of trust, and transforming community.
If you choose to participate, this outlines the process we will follow:
The facilitators will meet with each affected party privately to explain the program, to hear their perspective on what has happened, to explore what they are hoping for from the process, and then to determine if they want to participate in the restorative process. The facilitators will determine from these meetings with the parties choosing to be involved what the process will look like. This includes several possibilities such as: whether they will proceed to a face to face conference; a conciliated agreement; another specifically designed restorative intervention between the affected parties, or whether other responses outside of our agency would be more appropriate.
If it is determined that bringing the affected parties together would be appropriate and will do no further harm, a meeting (or several meetings) will be scheduled, and all parties who are ready and willing to participate will attend. This meeting is known as a “conference”. Affected Parties in most cases will have family members or other support people who attend and participate in the conference. Those affected by the incident and in some cases community members/stakeholders may participate provided they attend pre-meetings and are committed to a respectful, safe and restorative process. A team of two facilitators will guide the conference ensuring an atmosphere of safety and respect.
At the conference(s) each party will be asked to explain what happened from their perspective, and the details of the incident in question. Other participants will also have a chance to share their knowledge and understanding of the incident. Each person will have an opportunity to explain how the incident affected them, and how they feel about what happened. This is a time for people to voice their issues and concerns.
The facilitators will lead a discussion of the issues that have arisen from what is shared from the participants about the incident.
Following discussion will allow the parties to determine the best way to resolve the issues and any subsequent concerns or desired outcomes. This process of discussion and negotiation will produce what is known as a “Conference Agreement”, which through dialogue and consensus will be mutually agreed upon and then signed by everyone present. The agreement is intended to be restorative, proportionate, reasonable and fair as well as provide the opportunity for the person(s) responsible to make amends for the harms done and address the impacts.
Our Commitment
Our commitment to this process is to ensure that each participant is treated with the utmost care, dignity, and respect. It is important to understand that difficult feelings surrounding an experience are often needed to be expressed, and the conference should provide a safe and supportive context for this to occur. It is the hope and intention of restorative justice that all parties will view this experience as supportive and restorative in nature.
The police or other community based referring agency will be provided with a copy of the Conference Agreement. Should the responsible party withdraw from this process at any time or fail to fulfill the requirements of the Conference Agreement, this information will be shared with the referring agency and the information may be noted in their file accordingly. If the responsible party is found to be involved in any criminal activities while in this program, the opportunity to be part of Restorative Justice will be suspended, pending review by ARJAA and the referring agency.
Concerns or Complaints
If you have any concerns or complaints about your experience in the Restorative Justice process you may bring it to the attention of the Executive Director of Abbotsford Restorative Justice and Advocacy at ed@arjaa.org and/or the ARJAA Board of Directors Chairperson at BoardChair@arjaa.org
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Restorative justice looks at crime differently than the court process does. Restorative justice seeks to find ways for those affected by the crime to communicate and figure out what needs to happen to repair the harm, with the help of restorative justice facilitators.
-
Step One
After discussing the incident with both the harmed party and the responsible party, the police officer refers the case (if appropriate) to Restorative Justice. In the case of a minor, this will also be discussed with the youth or child’s parents.
Step Two
The person responsible and parents/guardians (if responsible party is a minor) will be contacted by ARJAA to determine if they are interested in proceeding with Restorative Justice.
Step Three
The harmed party will be contacted by ARJAA to determine if they are interested in proceeding with Restorative Justice.
Step Four
If both parties are willing, an initial private meeting will be set up with each of the parties to meet with the ARJAA team. This allows each party to discuss privately what happened, what the impacts have been, concerns are discussed, and each party is able to express what is needed to make things right. These meetings are confidential.
Step Five
After at least one initial meeting with each party, the ARJAA team determines whether the case is appropriate for mediation, or whether other approaches would be more effective.
Step Six
If the parties are ready for a face-to-face meeting, a mediated session called a conference is arranged. These are usually held at the APD Community Policing Office on Marshall Road at Abbotsford Way.
Step Seven
The conference takes place, involving all affected parties, and may also include people close to them who are needed for emotional support. A typical conference can take 2.5 hours. The conference is a confidential process. After a full discussion of the incident, and the concerns and issues that surround the incident, the goal is to draft an agreement that repairs the harm. This is very specific, and must show how restitution and amends will be made. It is developed and agreed up by the group, and signed by all parties. The mediators do not determine the agreement—they guide the process in which the participants will come up with the resolution that is needed.
Step Eight
The signed agreement is forwarded to the police and a copy is retained in the ARJAA file.
Step Nine
The person responsible for the incident fulfills the agreement, according to the time lines spelled out in the contract. This is supervised by ARJAA staff.
Step Ten
When the agreement is fulfilled the matter is completely concluded. A closing report is sent to the police, and there is no criminal record. The person responsible receives a closing letter.
EXCEPTIONS
Files are returned to police for further action if:
> The person responsible decides to withdraw from the process
> The person responsible fails to fulfill the agreement
> For some other reason the process cannot go forward
-
What happened?
How do you feel about what happened?
How were you impacted?
What has happened since the incident?
What has been the hardest thing?
What do you want the other people at the meeting to know about you and how you have been impacted?
Who else do you think has been affected by what happened? How do you think they have been affected?
What needs to happen for you to be able to begin to move forward from this and have resolution?
Do you have any questions for the other people who will be at the meeting?
What are your hopes moving forward?
-
Benefits for the harmed party
• Having a voice in more meaningful accountability for the person responsible
• Having a chance to be heard and understood
• Being able to express the impact of the crime, and the losses and harms sustained
• To ask questions and to receive information that can assist in closure and healing
Benefits for the responsible party
• The difficult, but important act of taking direct, personal responsibility for the offence
• The opportunity to experience, express and demonstrate genuine remorse
• The opportunity to make amends and provide restitution in a timely way
• The opportunity to learn from their experience
• The opportunity to put the offence behind them and move on with their lives through making meaningful amends.
-
This program is a voluntary program. If you decide that this process is not for you, ARJAA will forward the file back to the referring agency (APD or RCMP) and they decide how they want to move forward in dealing with it.
-
There are many reasons why an officer may wish to refer a case to a Restorative Justice program. Some of the benefits for the overall justice system include:
Meets the needs of crime victims and increases their sense of justice and satisfaction with the criminal justice system
Increases the public’s experience of justice and increases public satisfaction with the criminal justice system
Can decrease the time generally required to process offences in the traditional adversarial manner
Greatly decreases the expense of processing offences in the traditional manner by leveraging services from trained volunteers
Reduces incarceration costs by substituting creative alternatives for people who are not dangerous and can usefully contribute to the community and the victim
Reduces court dockets, caseloads, Crown counsel, defense counsel, correctional officers, and reduces the volume of police calls, making these resources more available for the cases that most need them
Increases the community’s understanding and ownership of the criminal justice process, as a result of victim and volunteer involvement
-
Our program is designed to provide facilitated restorative responses to harm that will enable the responsible party and the harmed party to meet in a safe, controlled environment. These Restorative Justice Conferences only take place after the ARJAA team has met with all the parties individually and assessed that it is safe and reasonable to proceed to a face-to-face meeting. The conference also enable the parents of a young person to be part of the restoration process, along with other members of the community who have been affected by the offence. Together, all conference participants (with the guidance of a trained facilitator) discuss and work together to create fair and proportionate resolution.
-
Any person responsible who completes restorative justice will not have a criminal record for the offense that led them to being referred.
Adverse police contact will only be listed if the person responsible is applying for a vulnerable sector check and it will state the offense type, the police file number, and that they were the subject of complaint or the suspect chargeable. A vulnerable sector check is only necessary for people applying to work with vulnerable groups ie. Children, people with disabilities, the elderly, etc). A standard criminal record check will not show adverse police contact.
The exceptions:
If the person responsible was a youth (ages12-17) at the time of the offense then adverse police contact will not be shown even if they are applying for a vulnerable sector check.
For adult persons responsible (those who committed the offense at ages 18 and up) adverse police contact for a vulnerable sector check will only be shown for the duration of each offense’s retention period. Each criminal offense has its own retention periods, for example: theft will show for 5 years and assault will show for 8 years. If there are questions about the retention periods for a particular offense check with ARJAA and we can inquire with the APD.
Retention Periods:
• Theft- 5 years
• Mischief- 5 years
• Fraud- 5 year
• Assault, assault with a weapon, assault causing bodily harm- 8 years
• Break and enter- 8 years
• Sexual assault- 20 years
-
Everything we talk about is confidential. The Abbotsford Police have a right to know who attends the meeting and will get a copy of the agreement at the end, but everything we discuss stays here. The only time we have to report something is if:
Someone is going to hurt themselves
Someone is going to hurt someone else
If a child is being abused
If a crime is going to be committed in the future